An Introduction to Serverless Architecture – learn what serverless architecture is, its benefits, components, and real-world use cases in this beginner’s guide.
An Introduction to Serverless Architecture
In the evolving world of cloud computing, An Introduction to Serverless Architecture provides a fresh perspective on how modern applications are built and deployed. For developers, architects, and businesses seeking efficiency, serverless architecture represents a fundamental shift from traditional infrastructure management to an event-driven, scalable model. This serverless beginners guide aims to simplify the core serverless concepts, explore its benefits, and highlight common use cases of serverless systems in today’s digital ecosystem.
What Is Serverless Architecture?
Serverless architecture is a cloud computing execution model where the cloud provider dynamically manages the allocation and provisioning of servers. Contrary to its name, it doesn’t mean there are no servers involved. Instead, developers are freed from managing them. With serverless technology, the responsibility of maintaining, scaling, and securing infrastructure shifts entirely to the cloud provider.
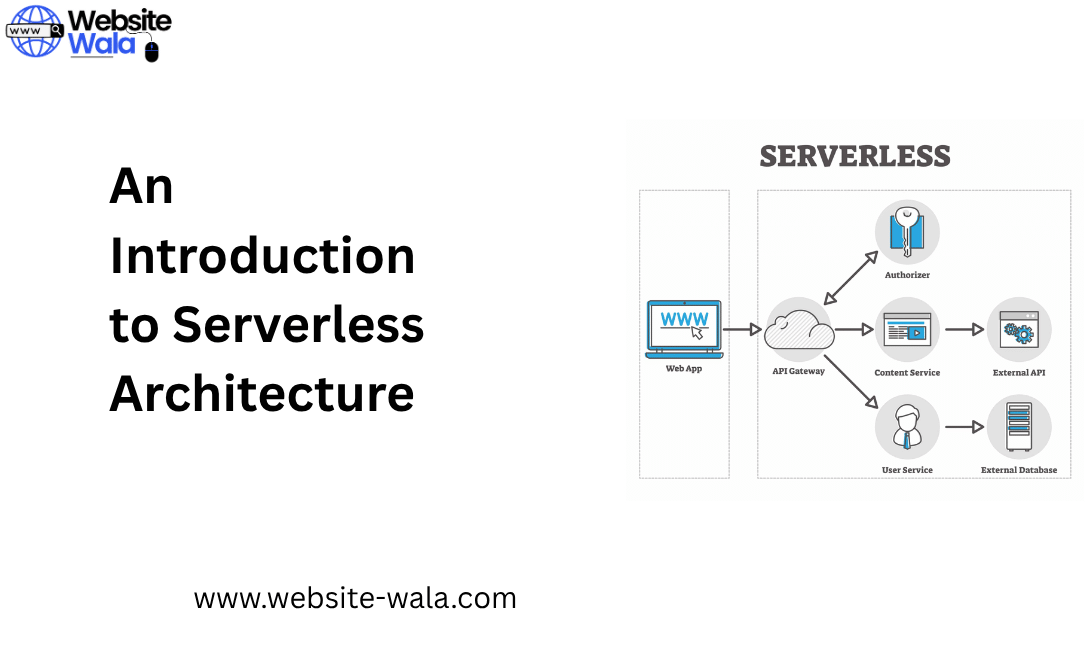
In An Introduction to Serverless Architecture, the focus is on understanding how developers can build applications by deploying functions—small, single-purpose pieces of code—that execute only when triggered by specific events. This model is often referred to as Functions-as-a-Service (FaaS) and is central to serverless computing.
Popular platforms such as AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions allow developers to run backend code in response to events without provisioning or managing servers.
A Brief Serverless Overview
Before the advent of serverless technology, deploying applications required managing physical or virtual servers. Developers had to handle provisioning, scaling, and uptime maintenance. The serverless overview changes this paradigm by allowing automatic scaling and pay-per-use billing.
This shift makes serverless development faster, more efficient, and cost-effective. Businesses can focus on innovation and core functionality rather than operational overhead.
In An Introduction to Serverless Architecture, understanding this transformation is key—organizations move from infrastructure management to pure code execution, reducing complexity while improving scalability.
Core Serverless Components
A crucial part of An Introduction to Serverless Architecture is understanding its primary building blocks. The following serverless components define how serverless applications operate:
-
Functions-as-a-Service (FaaS):
The core of serverless computing, FaaS allows developers to write functions triggered by specific events such as API calls, file uploads, or database updates. -
Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS):
These are third-party services such as authentication, databases, and storage integrated into applications without managing servers. -
Event Sources:
Triggers that invoke functions. These can be HTTP requests, message queues, or changes in data streams. -
APIs and Gateways:
API gateways serve as entry points for managing and routing requests to serverless components.
Understanding these elements in An Introduction to Serverless Architecture helps developers grasp how individual components interact to create a complete serverless application.
Benefits of Serverless Architecture
When discussing An Introduction to Serverless Architecture, the benefits of serverless play a crucial role in understanding why it has become a mainstream solution. Some of the key advantages include:
1. Cost Efficiency
You pay only for the resources consumed during execution. There’s no charge when your code isn’t running, significantly reducing costs compared to traditional infrastructure.
2. Automatic Scalability
Serverless technology automatically scales applications based on demand, handling spikes in traffic without manual intervention.
3. Faster Time to Market
By removing infrastructure concerns, serverless development allows teams to deploy features quickly, accelerating innovation and delivery.
4. Reduced Operational Overhead
Cloud providers handle server management, monitoring, and updates. This allows developers to focus entirely on writing and improving application logic.
5. Enhanced Reliability
Serverless computing runs across distributed infrastructure, reducing the risk of single points of failure and ensuring high availability.
These benefits of serverless demonstrate why the architecture is ideal for modern, agile software development environments.
Common Use Cases of Serverless
Another important part of An Introduction to Serverless Architecture is exploring the use cases of serverless applications. Some of the most common include:
-
Web and Mobile Backends:
Build responsive APIs using serverless components like API Gateways and FaaS for lightweight and scalable backend logic. -
Real-Time Data Processing:
Analyze and process data streams in real time, ideal for IoT, analytics, and log processing. -
Scheduled Tasks and Automation:
Run scheduled maintenance jobs, data backups, or periodic analytics using serverless functions. -
Chatbots and Voice Assistants:
Implement conversational interfaces and voice-driven applications that scale dynamically based on user requests. -
Microservices:
Create independent, event-driven microservices that enhance flexibility and reduce interdependencies in large systems.
Each of these use cases of serverless highlights its adaptability and ability to fit diverse application requirements.
Serverless Concepts Explained
A deeper understanding of serverless concepts reveals why this model is transforming software development. In An Introduction to Serverless Architecture, key concepts include:
-
Event-Driven Execution:
Code runs in response to triggers such as HTTP requests or file uploads. -
Statelessness:
Each function runs independently without maintaining a session or state between invocations. -
Cold Starts and Warm Starts:
A cold start occurs when a function runs for the first time, while warm starts refer to already-initialized instances for faster response. -
Observability and Monitoring:
Built-in tools for tracking logs, metrics, and performance to ensure smooth operations.
Understanding these serverless concepts helps serverless for beginners grasp how applications behave in a real-world environment.
Challenges of Serverless Development
While An Introduction to Serverless Architecture highlights its many advantages, it’s also important to address potential challenges in serverless development:
-
Cold Start Delays:
Functions may experience initial latency when they start from an idle state. -
Vendor Lock-In:
Different cloud providers use proprietary services, making migration complex. -
Debugging Complexity:
Distributed nature of serverless computing can make tracing and debugging harder. -
Resource Limitations:
Functions often have execution time and memory constraints that developers must manage efficiently.
Understanding these challenges ensures balanced expectations when adopting serverless technology.
The Future of Serverless Technology
The future of serverless architecture is promising. As enterprises embrace cloud-native approaches, serverless computing continues to evolve with improved performance, broader integrations, and enhanced developer tools.
In An Introduction to Serverless Architecture, it’s evident that the next wave of innovation will focus on combining serverless components with AI, machine learning, and edge computing. This will lead to more intelligent, responsive, and cost-efficient applications across industries.
Conclusion
An Introduction to Serverless Architecture offers an in-depth look into how serverless technology is reshaping the modern software landscape. From its core components and benefits to its practical use cases, this serverless beginners guide serves as a comprehensive resource for those exploring the potential of serverless development.
By embracing serverless computing, developers can build scalable, resilient, and efficient applications with minimal operational burden. Whether you’re a newcomer or an experienced engineer, understanding An Introduction to Serverless Architecture is the first step toward leveraging the next generation of cloud innovation.